Background
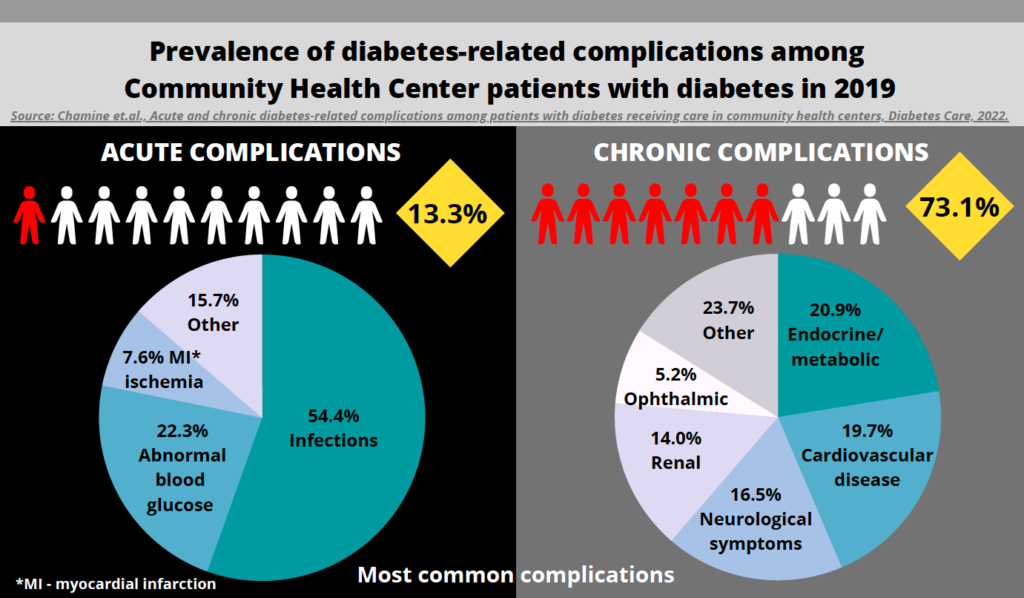
Diabetes-related complications may lead to greater health problems or death in patients with diabetes. Economically and socially vulnerable patients often receiving care at community health centers are at an increased risk for developing diabetes and diabetes complications. Understanding the prevalence of acute and chronic complications among these patients with diabetes, and the risk factors for developing complications can help clinics improve care for patients with diabetes. Using electronic health records from 64,739 patients, this work assessed the prevalence of acute and chronic complications and the risk factors for developing these complications among people with diabetes receiving care in community health centers in 2019.
Useful findings
The results show that in 2019 one in eight CHC patients with diabetes had a diagnosis of an acute complication, and about three quarters had a diagnosis of a chronic complication. Those with acute or chronic complications had a greater number of ambulatory visits and were more likely to experience comorbid mental health or physical health conditions than patients with diabetes not experiencing complications.
Bottom Line
These findings published in Diabetes Care highlight the significant burden of acute and chronic complications for CHC patients with diabetes and reinforce the need for increased and ongoing support for CHCs to improve accessibility and affordability of diabetes care for their patients.