Background
One in three Americans suffers from hypertension, a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Treatment and control of hypertension are important to prevent cardiovascular events and death. One of the important factors influencing hypertension medical care and control is access to health insurance. Many patients, especially patients with low-income, obtained health insurance coverage and thus gained access to hypertension treatment after the Affordable Care Act (ACA) Medicaid expansion. Another important factor that may influence hypertension control is neighborhood-level social deprivation. In this study, researchers investigated the influence of neighborhood-level social deprivation on the relationship between health insurance and hypertension control.
Useful Findings
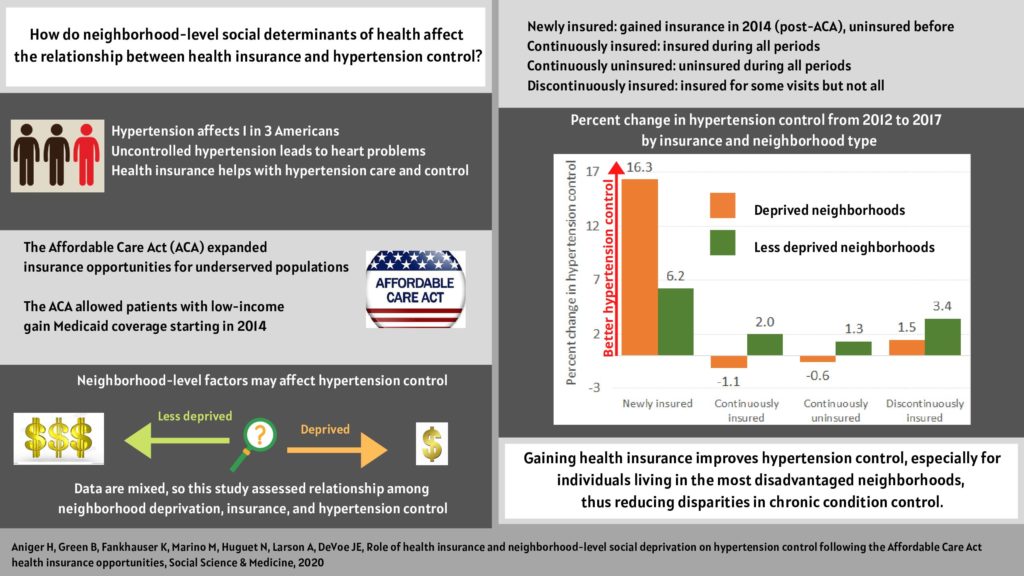
This study found that hypertension control improved for all groups regardless of insurance status, with the most gains among patients who were newly insured after the ACA. The greatest increase in hypertension control (16%) occurred among newly insured patients post-ACA living in the most deprived neighborhoods compared to those living in less deprived neighborhoods.
Bottom Line
This study published in the Social Science & Medicine found that gaining health insurance improves hypertension control especially for people living in disadvantaged neighborhoods. Overall, these findings suggest that focused efforts to improve hypertension control among the most disadvantaged populations can have a substantial impact on mortality and decrease disparities in adverse cardiovascular outcomes.